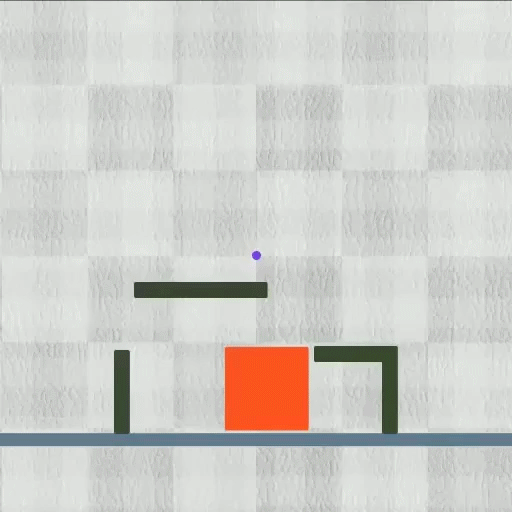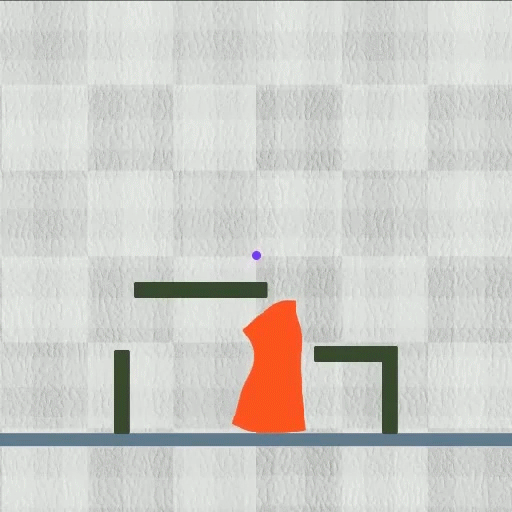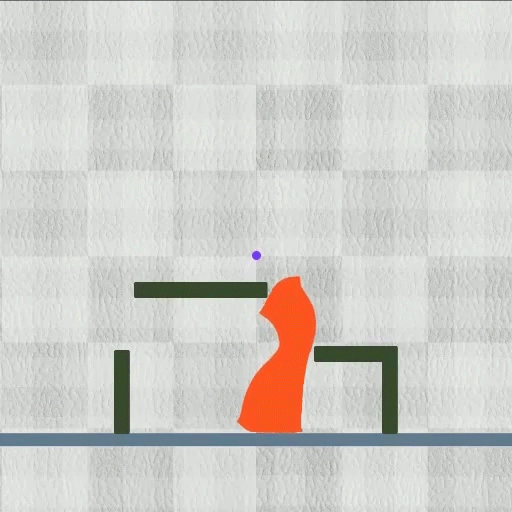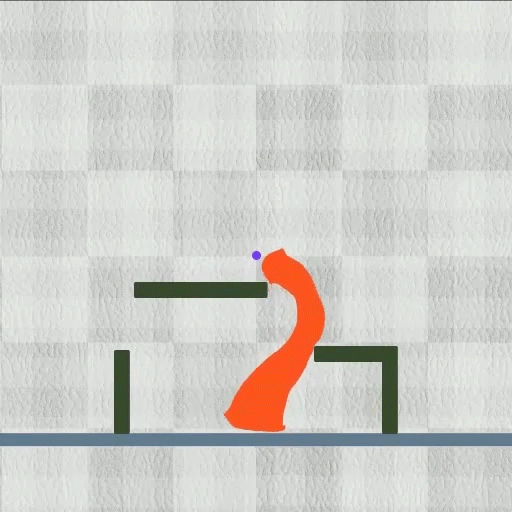
Picture a slime-like robotic that can effortlessly alter its form to press with slim areas, which can be released inside the body to get rid of an undesirable thing.
While such a robotic does not yet exist outside a lab, scientists are functioning to create reconfigurable soft robotics for applications in healthcare, wearable gadgets, and commercial systems.
Yet just how can one manage a squishy robotic that does not have joints, arm or legs, or fingers that can be adjusted, and rather can considerably modify its whole form at will? MIT scientists are functioning to address that inquiry.
They created a control formula that can autonomously discover just how to relocate, stretch, and form a reconfigurable robotic to finish a details job, also when that job calls for the robotic to alter its morphology numerous times. The group additionally constructed a simulator to examine control formulas for deformable soft robotics on a collection of tough, shape-changing jobs.
Their technique finished each of the 8 jobs they reviewed while outshining various other formulas. The method functioned particularly well on diverse jobs. For example, in one examination, the robotic needed to lower its elevation while expanding 2 little legs to press with a slim pipeline, and after that un-grow those legs and expand its upper body to open up the pipeline’s cover.
While reconfigurable soft robotics are still in their early stage, such a strategy can sooner or later make it possible for general-purpose robotics that can adjust their forms to complete varied jobs.
” When individuals consider soft robotics, they often tend to consider robotics that are flexible, yet go back to their initial form. Our robotic resembles sludge and can really alter its morphology. It is extremely striking that our technique functioned so well since we are handling something brand-new,” states Boyuan Chen, an electric design and computer technology (EECS) college student and co-author of a paper on this approach.
Chen’s co-authors consist of lead writer Suning Huang, an undergraduate trainee at Tsinghua College in China that finished this job while a seeing trainee at MIT; Huazhe Xu, an assistant teacher at Tsinghua College; and elderly writer Vincent Sitzmann, an assistant teacher of EECS at MIT that leads the Scene Depiction Team in the Computer Technology and Expert System Research Laboratory. The research study will certainly exist at the International Meeting on Discovering Representations.
Regulating vibrant activity
Researchers usually educate robotics to finish jobs utilizing a machine-learning technique referred to as support knowing, which is an experimental procedure in which the robotic is compensated for activities that relocate closer to an objective.
This can be reliable when the robotic’s relocating components correspond and distinct, like a gripper with 3 fingers. With a robot gripper, a support finding out formula could relocate one finger somewhat, finding out by experimentation whether that activity makes it a benefit. After that it would certainly go on to the following finger, and so forth.
Yet shape-shifting robotics, which are regulated by electromagnetic fields, can dynamically squeeze, flex, or extend their whole bodies.
发布者:Dr.Durant,转转请注明出处:https://robotalks.cn/a-better-way-to-control-shape-shifting-soft-robots/

