Greater than 100 million individuals in the USA experience metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver condition (MASLD), defined by an accumulation of fat in the liver. This problem can bring about the advancement of a lot more extreme liver condition that creates swelling and fibrosis.
In hopes of finding brand-new therapies for these liver conditions, MIT designers have actually made a brand-new sort of cells version that a lot more properly simulates the style of the liver, consisting of capillary and immune cells.
Coverage their searchings for today in Nature Communications, the scientists revealed that this version might properly duplicate the swelling and metabolic disorder that take place in the onset of liver condition. Such a tool might aid scientists recognize and evaluate brand-new medications to deal with those problems.
This is the most up to date research in a bigger initiative by this group to make use of these sorts of cells designs, likewise called microphysiological systems, to check out human liver biology, which can not be conveniently reproduced in computer mice or various other pets.
In an additional current paper, the scientists made use of an earlier variation of their liver cells version to check out just how the liver replies to resmetirom. This medication is made use of to deal with a sophisticated type of liver condition called metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), however it is just efficient in concerning 30 percent of people. The group discovered that the medication can cause an inflammatory feedback in liver cells, which might aid to clarify why it does not aid all people.
” There are currently cells designs that can make great preclinical forecasts of liver poisoning for sure medications, however we actually require to much better version condition states, due to the fact that currently we wish to recognize medication targets, we wish to confirm targets. We wish to check out whether a specific medication might be better very early or later on in the condition,” claims Linda Griffith, the Institution of Design Teacher of Training Development at MIT, a teacher of organic design and mechanical design, and the elderly writer of both researches.
Previous MIT postdoc Dominick Hellen is the lead writer of the resmetirom paper, whichappeared Jan. 14 in Communications Biology Erin Tevonian PhD ’25 and PhD prospect Ellen Kan, both in the Division of Biological Design, are the lead writers of today’s Nature Communications paper on the brand-new microphysiological system.
Designing medication feedback
In the Communications Biology paper, Griffith’s laboratory collaborated with a microfluidic tool that she initially established in the 1990s, called the LiverChip. This chip uses a basic scaffold for expanding 3D designs of liver cells from hepatocytes, the key cell key in the liver.
This chip is commonly made use of by pharmaceutical firms to evaluate whether their brand-new medications have negative results on the liver, which is a vital action in medication advancement due to the fact that the majority of medications are metabolized by the liver.
For the brand-new research, Griffith and her pupils customized the chip to make sure that maybe made use of to examine MASLD.
People with MASLD, an accumulation of fat in the liver, can ultimately create MASH, a much more extreme condition that takes place when mark cells called fibrosis types in the liver. Presently, resmetirom and the GLP-1 medication semaglutide are the only medicines that are FDA-approved to deal with MASH. Locating brand-new medications is a top priority, Griffith claims.
” You’re never ever proclaiming triumph with liver condition with one medication or one course of medications, due to the fact that over the long-term there might hold your horses that can not utilize them, or they might not work for all people,” she claims.
To produce a design of MASLD, the scientists subjected the cells to high degrees of insulin, together with huge amounts of sugar and fats. This resulted in an accumulation of fat and the advancement of insulin resistance, a characteristic that is frequently seen in MASLD people and can bring about kind 2 diabetes mellitus.
When that version was developed, the scientists dealt with the cells with resmetirom, a medicine that functions by simulating the results of thyroid hormonal agent, which promotes the failure of fat.
To their shock, the scientists discovered that this therapy might likewise bring about a boost in immune signaling and pens of swelling.
” Since resmetirom is mostly meant to decrease hepatic fibrosis in MASH, we discovered the outcome fairly paradoxical,” Hellen claims. “We presume this searching for might aid medical professionals and researchers alike comprehend why just a part of people react favorably to the thyromimetic medication. Nevertheless, added experiments are required to better clarify the underlying device.”
An even more practical liver version
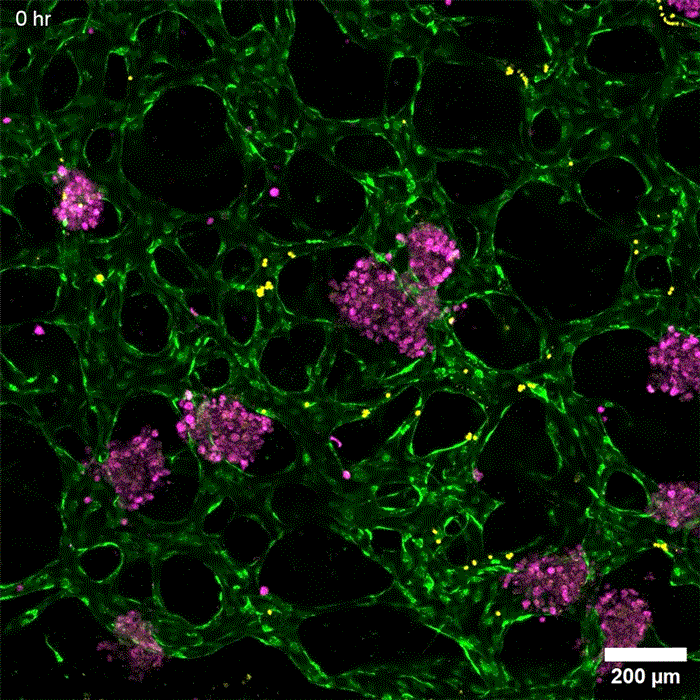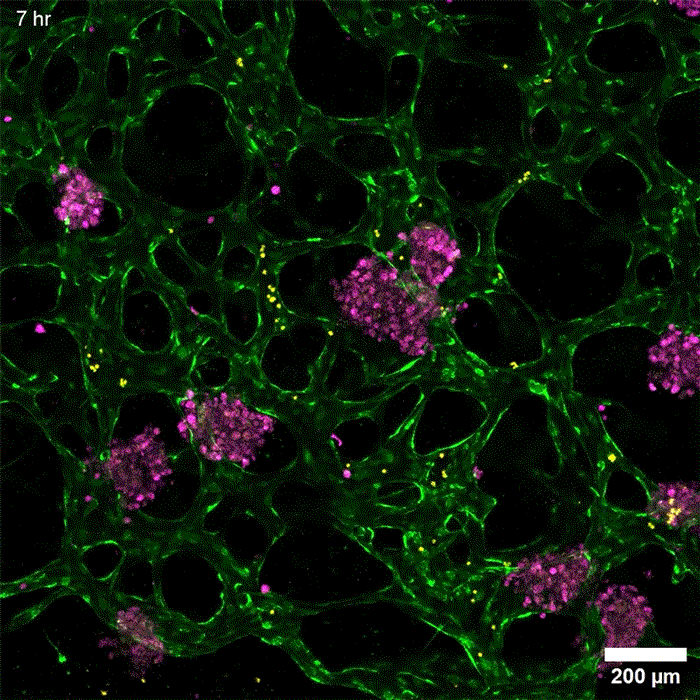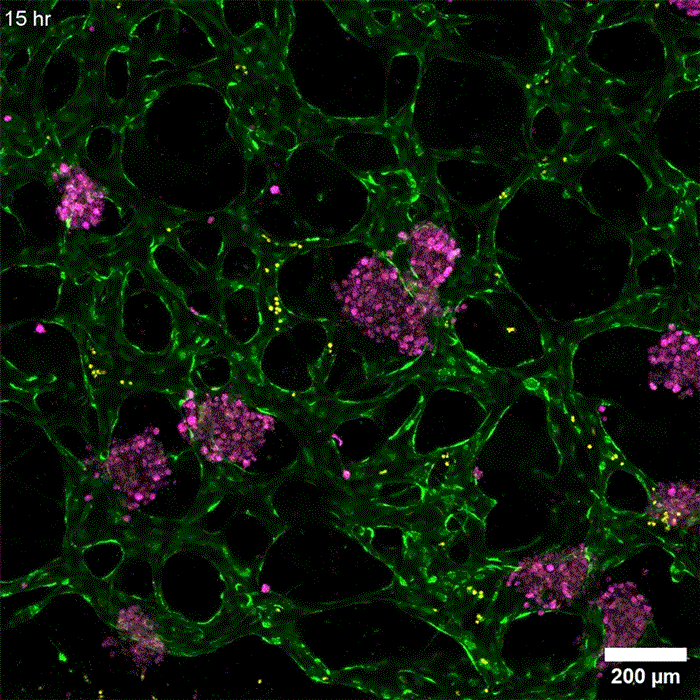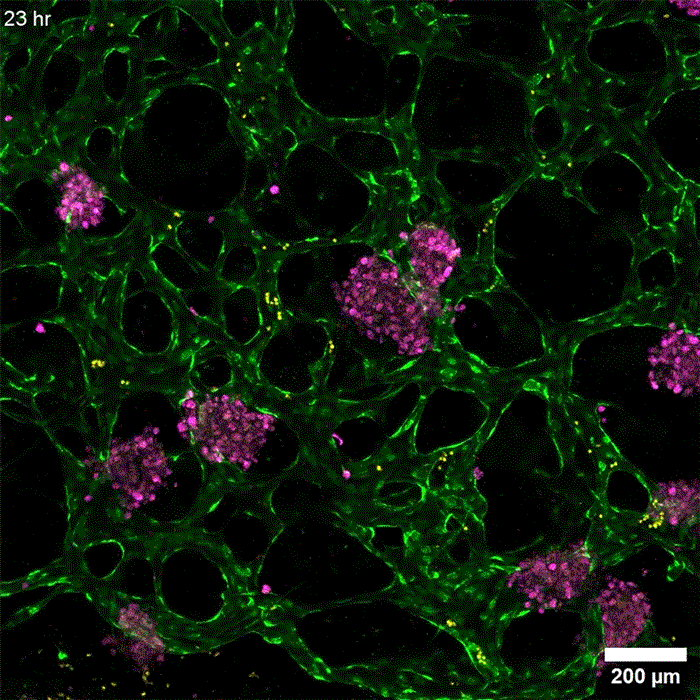
发布者:Dr.Durant,转转请注明出处:https://robotalks.cn/new-tissue-models-could-help-researchers-develop-drugs-for-liver-disease/

